by Sean Furey, Director – RWSN Secretariat @ Skat Foundation
Rural Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) is such a local, personal, issue that does global-level exchange make sense?
At first glance, rural areas and communities worldwide seem too diverse for networking and knowledge exchange to be useful or meaningful. What does WASH for isolated hamlets in the Nepalese Himalayas have in common with a fishing village on the Peruvian coast or a small town in northern Nigeria? Quite a lot, it turns out.
Last year, we were privileged to be approached by the Water Section at the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), to support them with an exciting programme called Sustainable and Innovative Rural Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (SIRWASH), funded by the Water Section of the Swiss Agency for Development & Cooperation (SDC). They asked us to help strengthen the sharing on rural WASH topics within the Latin America and Caribbean (LAC) region and to encourage South-South exchange between LAC, Africa and Asia. Thanks to our strategic partnership with SuSanA we felt well placed to do this, and a great opportunity for both networks to grow our membership in the LAC region and serve our members there better.
Multilateral Development Banks – amazing allies
When it comes to shear financial clout and convening power, Multi-lateral Development Banks (MDBs) are hard to beat, but even they have had mixed success with rural WASH – but there have been successes and they have recognised that they can learn from each other so that they can provide their client governments with the technical assistance and financial options to deliver sustained improvements. So, last year the relevant focal points from the African (AfDB), Asian (ADB) and Inter-American (IDB) met and agreed on a Call to Action with three priorities:
- Information-based decision-making and rural WASH investments and service monitoring.
- Institutional strengthening & coordination.
- Rural sanitation.
From this, we organised a webinar mini-series drawing on their recommendations for case studies on each topic from each region.
Finding the common threads and bringing them together to make them stronger
This year, we took more steps to build an understanding and appreciation of the solutions that have the potential to transcend the variability of local contexts and be adapted. With growing interest, our colleagues at the World Bank also joined the small group and together we organised a special SIRWASH breakfast meeting and an open session on “Coordinating Rural Water Investments to Promote Security and Stability” with REAL-Water :
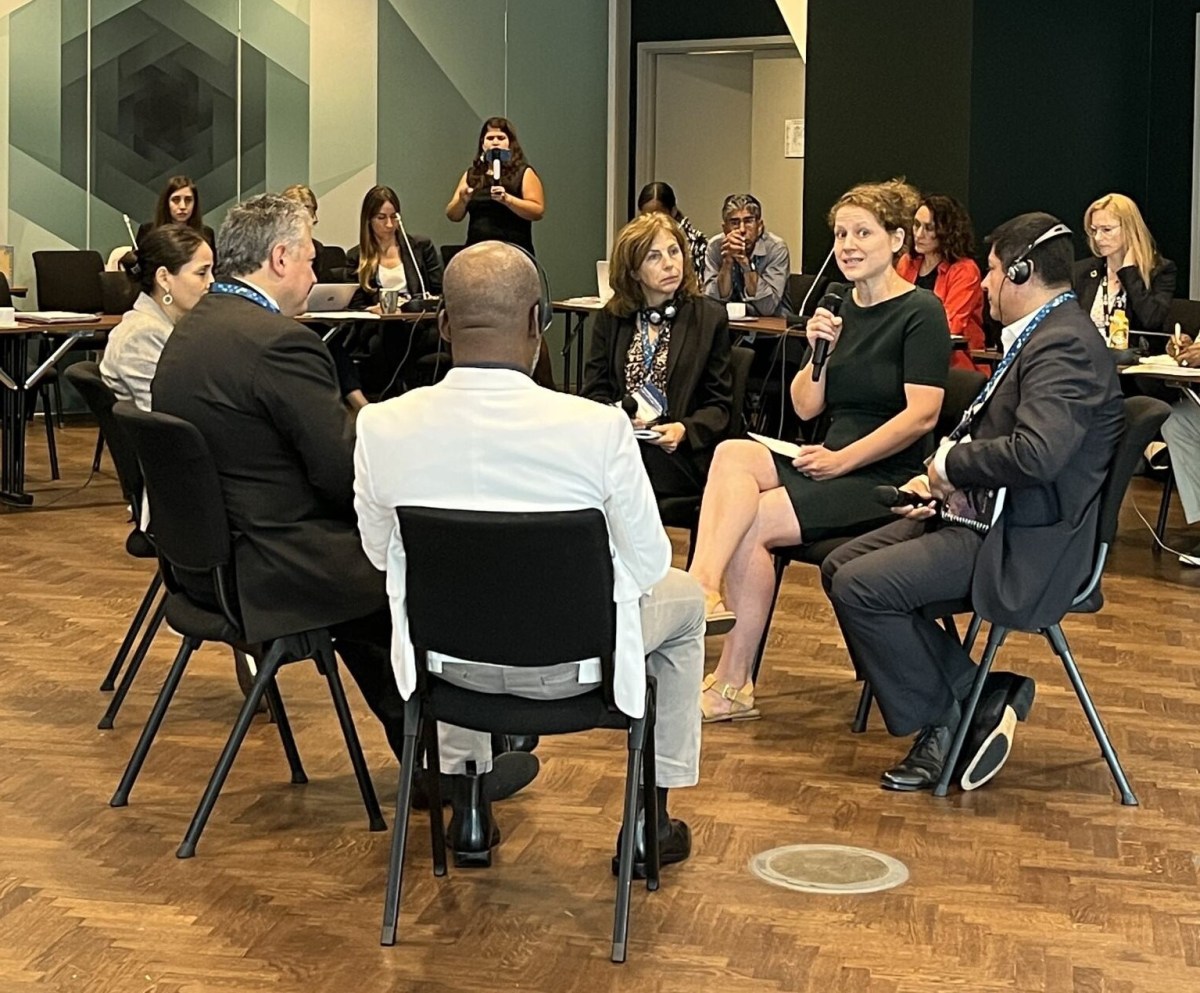
The SIRWASH breakfast meeting that followed was in the spirit of collaboration among countries in the global south, using knowledge sharing as a catalyst for innovative and sustainable solutions. It was attended by more than 40 representatives from countries (Haiti, Brazil, Peru, Chile, Nigeria and Uganda), multilateral banks, multilateral and bilateral agencies (SDC, AECID, SIDA, WHO, OAS, UNICEF), NGOs and philanthropists (including, One Drop, Water For People, Avina, Aguatuya, mWater, Global Water Center), as well as networks, partnerships and research (RWSN, SuSanA, WASH Agenda for Change, WASH Funders Group, SIWI, Uptime, the Aquaya Institute).
Using the “Fishbowl” method, participants exchanged their perspectives in an open and dynamic way on how strategic partnerships can increase impact in the sector. Discussions focused on two key questions:
1. How can technological innovations in rural WASH information systems be supported to be truly effective in decision making and incentivize scaling up?
2. What are practical solutions to improve the design and implementation of national rural WASH programs so that their benefits are sustained over the long term?
One of the central themes was innovation through sector information systems, a crucial tool for planning and managing water and sanitation services in rural areas. Three countries shared their experiences on how they have adapted and improved these systems:
- Haiti highlighted the use of information systems for decision-making;
- Nepal explored the potential of artificial intelligence in WASH;
The importance of institutionalizing information at the national level and ensuring that communities participate in the validation and appropriation of data and decisions was emphasized.
In addition to information systems, the event underscored the need to integrate both technological and social innovations to improve rural services. Social innovations and behavioural change are essential for communities to take ownership of the systems and actively participate in their management and maintenance. Participants agreed that long-term sustainability is about finding the sweet spot between community-ownership/responsibility and external support.
The second critical issue addressed was the sustainability of rural water and sanitation services. Participants stressed that the successful implementation of these services cannot depend solely on initial investments in infrastructure. Innovative mechanisms need to be developed to ensure their financing and continued operation. The examples of Brazil and Nigeria were instructive, both countries demonstrating how the combination of effective governance and innovative financial models can ensure the operational sustainability of services:
- Brazil presented its comprehensive implementation of their National Rural Sanitation Program (PNSR).
- Nigeria highlighted the ways a results-based SURWASH programme is strengthening institutional capacity.
- The Uptime Consortium shared their experiences and successes with Results-based Contracting on rural water service delivery across many contexts.
The discussion emphasized the need for functionality and quality indicators for rural services, linking reliable information to financial incentives for operators. This strategy can enhance the long-term sustainability of these systems. The working group concluded that collaboration is essential to ensure countries have reliable information for decision-making, aimed at improving the quality of rural services.r decision-making aimed at enhancing the quality of services in rural areas.
In the final discussion, consensus was reached on the need to create and maintain an enabling ecosystem for the development and sustainability of rural services. The great opportunity for development partners to join efforts and seek synergies, contributing technical and financial resources to this ecosystem in the countries was highlighted.
The event concluded with a clear call to action: all actors – governments, development banks, cooperation agencies, NGOs, networks and the private sector – must remain committed to financing and strengthening rural water and sanitation services. The MDBs will continue to work together on a concrete action plan to exchange and replicate successful and innovative experiences to ensure universal and quality WASH services in the countries.
Knowledge exchange is not just talk and powerpoint presentations, it is about building connections and trust between individuals and organisations, finding those common interests and encouraging co-creation of new insights and more sustainable solutions.
The symbolic activity organized by One Drop, where participants bonded to represent their intention to work together towards a common goal, was a powerful reminder of the importance of lasting partnerships. This symbolic gesture is just the beginning; it is essential to continue to scale up efforts so that the most vulnerable communities can access quality water and sanitation services in a sustainable and equitable manner.
Top-Down meets Bottom-Up
After this event, our partner Aguatuya convened an online meeting of Latin American WASH networks to encourage bottom-up exchange to complement our high-level approach. But we will follow that thread in the next post…
Many thanks to the large number of people involved, but in particular to Sergio Campos, Manuela Velasquez-Rodriguez and Cristina Mecerreyes at IDB; Diane Arjoon at AfDB, Vivek Raman and Tanya Huizer at ADB, Awa Diagne and Sarah Nedolast at the World Bank, Janine Kuriger at SDC, and to the wonderful RWSN/SuSanA team: Dr Aline Saraiva, Batima Tleulinova, Susanna Germanier, Lourdes Valenzuela, Paresh Chhajed, Chaiwe Sanderse and all the speakers and panellists for the webinars and sessions.