by Patrick Moriarty and Harold Lockwood
In the first post in this series, we explained why we believe that a paradigm shift is needed in the WASH sector: moving beyond the construction of physical hardware to the universal provision of safe drinking water (and sanitation) services worthy of the name.
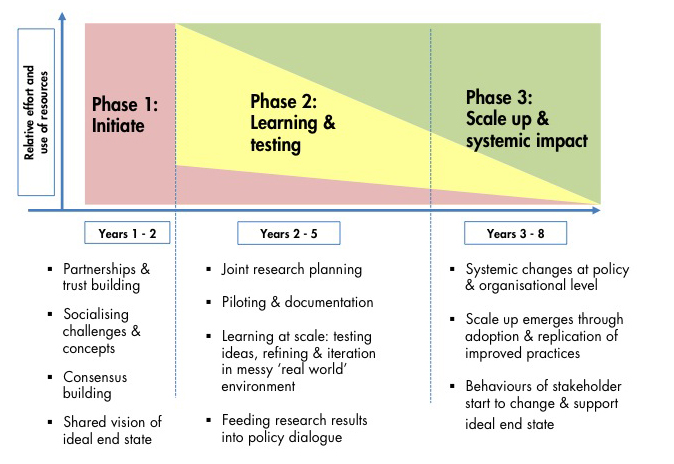
Because of the number of activities and actors involved, water and sanitation service delivery is inherently complex. And as much as we may be drawn to the idea of straightforward technological or market-based solutions, this complexity means such solutions will never get us all the way to sustainable services for everyone – particularly for the poorest people in the hardest to reach and most remote areas.
It is not enough that one individual or organisation begins to perform better or that an improvement is made in some technical aspect of service delivery. The whole system of individuals, organisations, technologies and…
View original post 1,220 more words