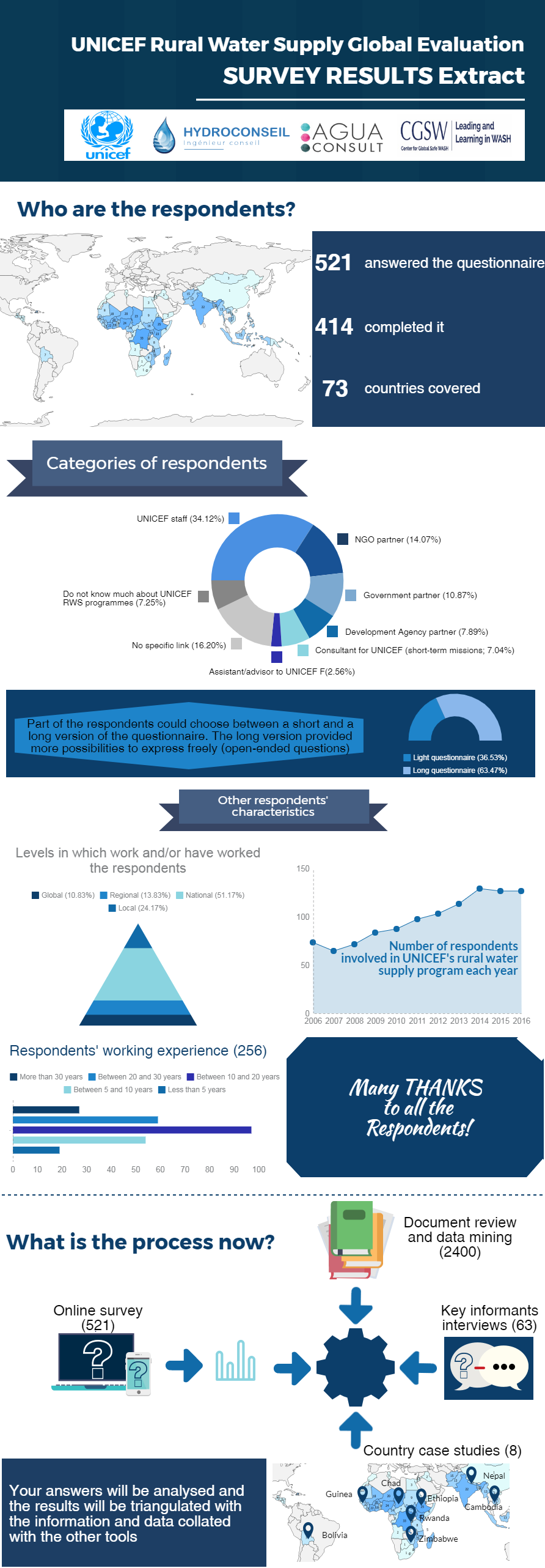
Stop the Rot at ZAWAFE 2023 Zambia – 1/4
This blog is part of a four-part series covering the presentations given at the 11th Zambia Water Forum and Exhibition. The event, themed “Accelerating Water Security and Sanitation Investments in Zambia: Towards Agenda 2023 through the Zambia Water Investment Programme”, lasted three days.
Our blog series takes a focused look at the presentations and discussions that revolved around “Addressing Rapid Hand Pump Corrosion in Zambia – Stop the Rot!”, which was co-convened by UNICEF and WaterAid, together with Ask for Water GmbH and the RWSN, hosted by Skat Foundation.
Cover Photo: Removal of corroding riser pipe in Hoima District, Uganda in 2012 (source: Larry Bentley). In 2018 the Government of Uganda issued a directive to prevent further use of galvanised iron riser pipes throughout the country.
First session:
History of the Rapid Hand Pump Corrosion Problems in Zambia and Potential Next Steps
In Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), an estimated 200 million people rely on a handpump for their main source of drinking water. They most likely use about 700,000 handpumps (Danert, 2022). Although the popularity of other technologies is growing, handpumps are likely to remain important in the region for decades to come, particularly in areas that are remote or with low population density. Unfortunately, many handpump services perform poorly or fail prematurely due to technical or installation defects with the borehole or the pump, as well as weaknesses with operation and maintenance or financial constraints.
In Zambia, it has been estimated that handpumps are the main source of drinking water for 19% of the urban and 32% of the rural population. It is worth to highlight that all metallic components that are submerged in water, or move in and out of water will eventually corrode, and so corrosion must be considered as part of the long-term maintenance of water wells with handpumps (or motorised pumps).
About rapid handpump corrosion
Rapid handpump corrosion occurs when aggressive groundwater reacts with galvanised iron (GI) riser pipes and rods of a handpump, and the India Mark II in particular. The materials corrode, with the pumped water becoming bitter in taste, with an unpleasant smell and a rusty colour. This not only renders the water unfit for drinking from a user perspective but also considerably reduces the pump lifespan. In Zambia, the main cause of rapid handpump corrosion is contact between groundwater with a pH of less than 6.5 and GI pipes and rods. However, salinity is also a problem in some parts of the country and can result in rapid corrosion too.
The use of alternative materials to GI, particularly stainless steel (SS) riser pipes and rods and uPVC rider pipes fitted with stainless steel connectors, can prevent rapid handpump corrosion. While rapid handpump corrosion was documented in West Africa in the late 1980’s ((Langenegger, 1989), and actions to prevent it have been taken in some places, the phenomenon still occurs in over 20 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Zambia, with an estimated 22,000 handpumps in use, serving 32% of the population with their main drinking water supply, is among these countries.
Figure 1: Soil reaction map (pH) map of Zambia, 2014. (Shitumbanuma et all, 2021)
Figure 2: Zambia’s Agro-Ecological Zones (1987) and the 10 Provinces (Makondo & Thomas, 2020)
Figure 3: History of efforts in Zambia in relation to rapid handpump corrosion – Overview
In Zambia, while the geographical extent of aggressive water is not fully understood by water sector professionals, it has been documented and explained with respect to soils. A Soil Survey by the Mount Makulu Research Station from 1990 presents the situation clearly, with extreme soil acidity in the north, and soil acidity in the central parts of the country. Further, in Zambia the traditional Chitemene – ‘slash and burn’ – method of cultivation in the high rainfall region has been used since time immemorial to neutralise low pH in soils in order to cultivate crops. Leaching from these highly acidic soils affects the pH of the groundwater.
The problem of rapid corrosion in handpumps in Zambia has been known for more than 30 years (Pitcher, 2001) and is well documented, including in the following:
- The Central Province Rural Water Supply Project (CPRWSP) (1985 – 1996) – which installed 564 handpumps with stainless steel riser pipes rather than using GI to prevent rapid corrosion.
- The North-Western Province Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Project (2004 – 2009) – over 350 handpumps were installed with stainless steel riser pipes, also in response to the same issue.
- In Luapula Province under the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)-supported Groundwater Development Project (2007 – 2010), some Afridev handpumps with uPVC riser pipes were installed. The project rehabilitated existing, corroded handpumps which the community had previously abandoned. Replacing the GI pipes with uPVC stopped the iron problem, indicating that in these boreholes, using iron pipes had been the cause of corrosion. Iron removal plants were also installed on some boreholes.
However, while solutions were implemented at scale in the aforementioned projects in Central and North-Western Provinces, as well as the study in Luapula, the use of GI riser pipes and rods still continued in subsequent projects in the same areas.
Some stepbacks
- There was a change in the ministry responsible for drilling works. The period 1985 – 1996 saw borehole drilling under the Department of Water Affairs, while the Department of Infrastructure and Support Services under the Ministry of Local Government and Housing took on this role after it had been created in 1995.
- National Guidelines for Sustainable Operation and Maintenance of Handpumps in Rural Areas (MLGH, 2007) includes neither aggressive water as a criterion for handpump selection nor the use of stainless steel riser pipes, and so the use of GI pipes in aggressive water as the cause of the ensuing rapid corrosion was in effect further supported.
Initiatives undertaken in the last 10 years
- Under the SOMAP 2 project (2012 – 2013), the JICA-supported programme carried out pipe replacement of GI at 20 sites in four provinces (Luapula, Copperbelt, Central and the North Western) whereby GI pipes were removed, the boreholes flushed and then installed with uPVC pipes. The replaced handpumps performed well without the water turning rusty, and the communities continued to draw water from them, whereas previously they had been abandoned.
- UNICEF also carried out pipe replacement in Mansa and Milenge districts of Luapula Province. In the study, India Mark II handpumps GI pipes at 45 sites were replaced with uPVC riser pipes. After the pipe replacement of GI riser pipes, the community used the handpumps that had previously been abandoned, with unsafe water sources being used instead. The pipe replacement study was successful, with the water users returning to previously abandoned boreholes which had clear, rust-free water.
- There is some evidence of other projects and organisations starting to use either stainless steel riser pipes, or uPVC riser pipes with stainless steel connectors in their projects, but documentation is limited. While stainless steel riser pipes have been used effectively, there are also some outstanding technical issues – particularly in relation to the removal of narrower diameter riser pipes, which require suitable tools that are not in the standard India Mark II toolkit. Further, the use of uPVC pipes has also been found to be problematic, as they need to be cut on removal and cannot easily be re-threaded. However, at least one NGO in Zambia has been using an alternative, comprising uPVC with stainless steel couplers which is available on the Zambian market. A further complication is that some parts of Zambia appear to exhibit naturally occurring iron. Tests are available to determine whether iron is naturally occurring or a result of corrosion, but there is no comprehensive map to indicate areas at risk of high levels of geogenic iron.
While stainless steel riser pipes have been used effectively, there are also some outstanding technical issues – particularly in relation to the removal of narrower diameter riser pipes, which require suitable tools that are not in the standard India Mark II toolkit. Further, the use of uPVC pipes has also been found to be problematic, as they need to be cut on removal and cannot easily be re-threaded. However, at least one NGO in Zambia has been using an alternative, comprising uPVC with stainless steel couplers which is available on the Zambian market. A further complication is that some parts of Zambia appear to exhibit naturally occurring iron. Tests are available to determine whether iron is naturally occurring or a result of corrosion, but there is no comprehensive map to indicate areas at risk of high levels of geogenic iron. Despite all of the efforts to date, and notwithstanding the widespread nature of rapid handpump corrosion of GI riser pipes and pump rods, the problem still persists in 2023.
Potential Next Steps for GRZ / International Donor Community / Universities
- Revise the National Water Policy to include aggressive groundwater in community boreholes
- Restrict Types of Handpumps to Certain Regions.
- Enact a Law and a Statutory Instrument on Aggressive Groundwater in Community Boreholes.
- Incentivise the private sector for provision of corrosion-resistant pipes and rods
- Regulation of Quality of Handpumps by Zambia Bureau of Standards.
- Standardise Handpumps Used in Zambia.
- Further studies and replacement of galvanised iron riser pipes.
- Further Research Studies on the phenomenon of naturally occurring iron in ground and surface water and
- Research Studies on Saline Water in Western Province
You are invited to access the presentations HERE, along with the session’s concept and the study report: Nkhosi. J and Danert, K. (2023). ‘Stop the Rot: History of the Rapid Handpump Corrosion Problem in Zambia and Potential Next Steps. Action research on handpump component quality and corrosion in sub-Saharan Africa’. Ask for Water GmbH, Skat Foundation and RWSN, St Gallen, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.27489.28006.
If you would like to dive deeper into the enriching exploration of water challenges and solutions through the Stop the Rot initiative, visit this page.
About the author:
Javan Nkhosi presenting at ZAWAFE 2023
Javan Nkhosi is a Zambian water professional. He has worked in the rural water sub-sector for more than 25 years on many water supply projects funded by the government, NGOs and donor agencies as a private consultant across Zambia. He has a passion for improving water supply to the unreached areas of rural Zambia. He holds a Diploma in Agricultural Engineering from NRDC, Lusaka, Advanced Diploma in Water Engineering from the Copperbelt University and an MSc in Project Management from the University of Lusaka. He is a Registered Engineer with Engineering Institute of Zambia (EIZ) and also a member of the Association of Consulting Engineers of Zambia (ACEZ) , an affiliate of the International Federation of Consulting Engineers (FIDIC).
References:
- Danert, K. (2022) ‘Stop the Rot Report I: Handpump reliance, functionality and technical failure. Action research on handpump component quality and corrosion in sub-Saharan Africa’. Ask for Water GmbH, Skat Foundation and RWSN, St Gallen, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.19733.81121
- Langenegger, O. (1989) ‘Groundwater quality: An important factor for selecting handpumps’. Developments in Water Science 39: 531–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5648(08)70561-6.
- Makondo, Cuthbert & Thomas, David. (2020). Seasonal and intra-seasonal rainfall and drought characteristics as indicators of climate change and variability in Southern Africa: a focus on Kabwe and Livingstone in Zambia. Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 140. 10.1007/s00704-019-03029-x.
- MLGH, 2007. National Guidelines for Sustainable Operation and Maintenance of Handpumps in Rural Areas, Republic of Zambia, Lusaka. https://www.rural-water-supply.net/en/resources/221
- Pitcher, F. 2001. India Mark II maintenance systems. in: Scott, R. (ed). People and systems for water, sanitation and health: Proceedings of the 27th WEDC International Conference, Lusaka, Zambia, 20-24 August 2001, pp. 433-435 https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/articles/conference_contribution/India_Mark_II_maintenance_systems/9591629
- Shitumbanuma, Victor & Simfukwe, Paul & Kalala, Daniel & Kaninga, Belinda & Gondwe, Brian & Nambala, Mupande & Kabwe, Stephen & Siulemba, Geofrey & Kapulu, Ndashe & Lungu, Obed & Mutegi, James. (2021). Integrated Soil Fertility Management in Zambia i The Zambia Soil Health Consortium Integrated Soil Fertility Management in Zambia.